前面章节我们自己定义了工具调用类
| class BasicToolNode:
def __init__(self, tools: list) -> None:
self.tools_by_name = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
def __call__(self, inputs: State):
messages = inputs.get("messages", [])
if messages:
message = messages[-1]
else:
raise ValueError("No message found in input")
outputs = []
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
tool_result = self.tools_by_name[tool_call["name"]].invoke(
tool_call["args"]
)
outputs.append(
ToolMessage(
content=json.dumps(tool_result),
name=tool_call["name"],
tool_call_id=tool_call["id"],
)
)
return {"messages": outputs}
|
这个类需要我们自己来实现,LangGraph 考虑到有大量的工具调用场景,所以LangGraph 提供了 ToolNode 类来简化客户端工具调用。我们来看一下它是如何工作的。工具还是使用上一章节中使用高德天气查询工具。
| from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool
import requests
class GaoDeWeather(BaseTool):
"""
高德天气查询
"""
name: str = "高德天气查询"
description: str = "高德天气查询,输入城市名,返回该城市的天气情况,例如:北京"
args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = GaoDeWeatherInput
return_direct: bool = True
api_key: str
def _run(self, city):
s = requests.session()
api_domain = 'https://restapi.amap.com/v3'
url = f"{api_domain}/config/district?keywords={city}"f"&subdistrict=0&extensions=base&key={self.api_key}"
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf-8"}
city_response = s.request(method='GET', headers=headers, url=url)
City_data = city_response.json()
if city_response.status_code != 200 or City_data.get('info') != 'OK':
return "没有查询到该城市的代码"
if len(City_data.get('districts')) <= 0:
return "没有获取到该城市的代码"
CityCode = City_data['districts'][0]['adcode']
weather_url = f"{api_domain}/weather/weatherInfo?city={CityCode}&extensions=all&key={self.api_key}"
weatherInfo_response = s.request(method='GET', url=weather_url)
weatherInfo_data = weatherInfo_response.json()
if weatherInfo_response.status_code != 200 or weatherInfo_data.get('info') != 'OK':
return "查询天气信息失败"
contents = []
if len(weatherInfo_data.get('forecasts')) <= 0:
return "没有获取到该城市的天气信息"
for item in weatherInfo_data['forecasts'][0]['casts']:
content = {
'date': item.get('date'),
'week': item.get('week'),
'dayweather': item.get('dayweather'),
'daytemp_float': item.get('daytemp_float'),
'daywind': item.get('daywind'),
'nightweather': item.get('nightweather'),
'nighttemp_float': item.get('nighttemp_float')
}
contents.append(content)
s.close()
return contents
|
一、手动调用工具
| from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
weather_tool = GaoDeWeather(api_key='xxxx')
tools = [weather_tool]
toolnode = ToolNode(tools)
ai_messsage = AIMessage(
content="",
tool_calls=[
{
"name": "高德天气查询",
"args": {
"city": "上海"
},
"id": "call_e8c34802b3904571bfeee7",
"type": "tool_call"
}
]
)
result = toolnode.invoke({"messages": [ai_messsage]})
print(result)
|
先使用 weather_tool = GaoDeWeather(api_key='xxxx') 来定义一个天气查询工具对象,然后将这个对象放到一个列表中,tools = [weather_tool], 目前这个列表只有一个工具,我们之后可以添加更多的工具,如前面文章使用的 tavily 搜索工具。
然后使用 toolnode = ToolNode(tools) 来定义ToolNode 对象,这个类初始化的时候需要传入工具的列表。
之后我们手工定义一个 AIMessage 对象, 这里传入 tool_calls 属性, 是个列表,列表为工具调用时需要的名称和参数,目前这个AIMessage 是自己定义的,之后会由大模型来生成。
定义好 AIMessage 对象以后,使用 toolnode.invoke({"messages": [ai_messsage]}) 来真正的调用工具,这时我们不用像BasicToolNode 中的 __call__ 方法中那样,自己来解析 tool_calls 参数,自己调用工具,这些操作完全由 ToolNode 类自己实现。
最终得到的结果为
| {'messages': [ToolMessage(content='[{"date": "2024-12-17", "week": "2", "dayweather": "晴", "daytemp_float": "13.0", "daywind": "北", "nightweather": "晴", "nighttemp_float": "4.0"}, {"d
ate": "2024-12-18", "week": "3", "dayweather": "晴", "daytemp_float": "8.0", "daywind": "北", "nightweather": "晴", "nighttemp_float": "4.0"}, {"date": "2024-12-19", "week": "4", "daywea
ther": "多云", "daytemp_float": "8.0", "daywind": "北", "nightweather": "阴", "nighttemp_float": "5.0"}, {"date": "2024-12-20", "week": "5", "dayweather": "多云", "daytemp_float": "10.0", "daywind": "北", "nightweather": "晴", "nighttemp_float": "4.0"}]', name='高德天气查询', tool_call_id='call_e8c34802b3904571bfeee7')]}
|
二、多工具调用
上面的代码展示了ToolNode 如何进行工具调用,注意到,AIMessage 类中的 tool_calls 是一个列表,意味着,真实的大模型返回的工具调用可能是多个,我们还是结合tavily 工具,看看多工具是如何调用的?
| from langchain_community.tools import TavilySearchResults
# 初始化两个工具
weather_tool = GaoDeWeather(api_key='xxxx')
tavily_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=2)
tools = [weather_tool, tavily_tool]
# 初始化 ToolNode 对象
toolnode = ToolNode(tools)
# AIMessage 中的 tool_calls 定义两个工具调用
ai_messsage = AIMessage(
content="",
tool_calls=[
{
"name": "高德天气查询",
"args": {
"city": "上海"
},
"id": "call_e8c34802b3904571bfeee7",
"type": "tool_call"
},
{
"name": "tavily_search_results_json",
"args": {
"query": "tesla 新款 Model Y 新特性"
},
"id": "call_e8c34802b3904571bfeee7",
"type": "tool_call"
}
]
)
result = toolnode.invoke({"messages": [ai_messsage]})
print(result)
|
上面代码中定义了两个工具 weather_tool 和 tavily_tool,在 AIMessage 的 tool_calls 中定义了两个工具调用。最终使用 toolnode.invoke({"messages": [ai_messsage]}) 来真正的进行工具调用,此时ToolNode 会根据 tool_calls 中的工具调用信息自动进行调用。 得到两个结果的返回,上面代码返回为
| {'messages': [
ToolMessage(content='[{"date": "2024-12-17", "week": "2", "dayweather": "晴", "daytemp_float": "13.0", "daywind": "北", ....}]', name='高德天气查询', tool_call_id='call_e8c34802b3904571bfeee7'),
ToolMessage(content='[{"url": "https://news.qq.com/rain/a/20241025A05IIC00", "content": "新款Model Y带来“七大杀手锏”!能满足国人的口味吗?_腾讯新闻 更多 正在浏览:新款Model Y带来“七大杀手锏”!能满足国人的口味吗? ....'response_time': 2.75})]}
|
三、大模型工具调用
上面的AIMessage 是我们手工写上去的,其中tool_calls 字段是按照AIMessage中tool_calls字段的定义模拟出来的,真实的系统应该是有大模型生成,结构也是这样的,本节我们来使用大模型真实的进行 tool_call 。
| # 初始化两个工具
weather_tool = GaoDeWeather(api_key='xxx')
tavily_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=2)
tools = [weather_tool, tavily_tool]
# 初始化 ToolNode
toolnode = ToolNode(tools)
# 初始化llm
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model_name="qwen-turbo",
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=1024,
top_p=1,
openai_api_key="sk-xxxx",
openai_api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1"
)
# 绑定工具到大模型
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
# 初始化用户提问
messages = [
HumanMessage(content="我晚上要去杭州,需要穿什么衣服?")
]
ai_message = llm_with_tools.invoke(messages)
messages.append(ai_message)
if ai_message.tool_calls:
tool_result = toolnode.invoke({"messages": [ai_message]})
messages.extend(tool_result.get("messages"))
# 再次进行大模型调用
final_result = llm_with_tools.invoke(messages)
print(final_result.content)
else:
print(ai_message.content)
|
上面代码使用大模型来真正的进行分析调用。
- 第一次使用
ai_message = llm_with_tools.invoke(messages) 获取大模型的工具调用分析
- 如果大模型的返回值中有 tool_calls, 则使用
toolnode.invoke({"messages": [ai_message]}) 来进行工具的调用
- 拿到工具的调用结果,与之前的消息再次请求大模型进行最终问题的总结回答
上面代码得到的输出为
晚上在杭州的天气预报显示,接下来几天的气温较低。具体来说,今天的温度会在3°C左右,而未来几日的夜间温度也都在1°C到7°C之间。因此,建议您穿上保暖的衣服,如毛衣和厚外套,并考虑搭配围巾和手套 以应对较低的温度。如果有雨具的话最好也带上,以防止突然的降雨或雾气。
理解了ToolNode 的运行原理,我们可以很快的使用 LangGraph 构建出运行图
| from typing import Type, TypedDict, Annotated
from langgraph.graph import add_messages, StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage, HumanMessage, AIMessage
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
weather_tool = GaoDeWeather(api_key='xxxx')
tavily_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=2)
tools = [weather_tool, tavily_tool]
toolnode = ToolNode(tools)
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model_name="qwen-turbo",
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=1024,
top_p=1,
openai_api_key="sk-xxxx",
openai_api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1"
)
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
def chatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
def condition_tools(state: State):
ai_message = state["messages"][-1]
if ai_message.tool_calls:
print(json.dumps(ai_message.tool_calls, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
return "tools"
return END
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
# 添加节点
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", toolnode)
# 添加边
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("chatbot", condition_tools)
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
app = graph_builder.compile()
inputs = {"messages": [HumanMessage(content="我今天要去杭州玩,那里的天气如何? 有什么好玩的?")]}
result = app.invoke(inputs)
print(result.get("messages")[-1].content)
|
这里添加工具节点只需要 graph_builder.add_node("tools", toolnode) 即可,其他的代码和前面代码几乎是一样的。
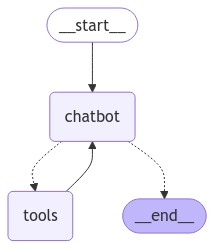
这里的tools 和 chatbot 进行反复的调用,其实这也就形成了一个可以自我反思的 ReAct 智能体。
这里,我问的问题是
我今天要去杭州玩,那里的天气如何? 有什么好玩的?
很显然,需要查询天气和调用搜索,但是这个tool calls 受大模型能力的影响很大,就代码中使用的qwen-turbo 模型来讲,还不能一次性的返回多个工具调用参数,它是分两次返回的。
| [
{
"name": "高德天气查询",
"args": {
"city": "杭州"
},
"id": "call_bf011943321e4b77a82320",
"type": "tool_call"
}
]
[
{
"name": "tavily_search_results_json",
"args": {
"query": "杭州 游将"
},
"id": "call_02ecadd5d148420c9bb0e0",
"type": "tool_call"
}
]
### 杭州今天的天气
从未来几天的天气预报来看,杭州今天(2024年12月17日)是多云天气,最高温度为13℃,最低温度为3℃。建议准备外套保暖,并且由于是多云天气,可考虑携带雨具,以备不时之需。
### 未来几天的天气预报:
- **12月18日**:全天多云转阴,最高温度9℃,最低温度1℃。
- **12月19日**:白天阴天到多云,最高温度7℃,夜间多云,最低温度1℃。
- **12月20日**:晴朗,气温逐渐回升,最高温度10℃,最低温度1℃。
### 杭州游玩推荐
根据搜索结果,没有直接找到关于旅游景点的信息。但是杭州作为中国著名的历史文化名城,拥有许多著名的旅游景点如西湖、灵隐寺等。你可以考虑参观这些地方来体验杭州的历史文化底蕴和自然风光。同时,可以探索一些新兴的网络热门地点,比如由“杭州将游网络科技有限公司”等推广的新型旅游打卡地。不过,更详细的旅游信息可能需要进一步查找或参考专业的旅游指南。
|
五、总结
本问介绍使用 ToolNode 作为LangGraph 节点来执行工具的调用过程,先使用人工模拟tool_calls 数据来展示 ToolNode 是如何进行工具调用的,然后又结合大模型来真正的进行模型调用。
